When talking about on-page SEO, there are a lot of myths, outdated techniques and just plain wrong information floating around the internet.
Today I wanted to share with you a quick checklist of some solid on-page SEO strategies you can start putting into practice immediately. Even if you only use a few of these, you’ll be better off than most.
Start Your Title Tag with Your Target Keyword
Google evaluates and gives weight to each word in your title tag. The longer your title is, the less weight each word gets. Also, words at the beginning get more weight than words found at the end.

Notice the top 3 results for “Photography Tips” all begin with that keyword phrase. To get the most out of your tag, keep it short (40 – 50 characters) and start with your target keyword or phrase.
Use Your Target Keyword or Phrase in the First 100 Words
Like your title tag, Google pays attention to where words are in the body of an article. Using your target keyword or phrase towards the beginning of an article helps to identify that it is an important idea within your post.
You’ll notice that the first paragraph of this post uses the phrase “on-page SEO.” While you don’t want to go overboard using your keyword or phrase, if you use it naturally near the beginning of your post, you’ll be good.
Don’t Use Your Keyword Too Much
Google uses a pretty advanced algorithm to understand what web pages are about. You don’t need to go crazy using your target keyword to convenience Google of the topic of your post. In fact, the ideal keyword density for a post is less than 5%. If we do some quick math, that means in a 2000 word post, you should mention your keyword less than 100 times.
Using your keyword too much is “keyword stuffing” and Google frowns on that.
Use Your Target Keyword In Your H1 Tag
The H1 tag is your highest-level heading tag on your page and should appear only once per page.
Consider a Newspaper article. By reading the headline of an article in a newspaper, you have a decent idea of what the article is about. Your H1 tag is like a newspaper article headline. Keep it short and make sure it conveys the topic of your post/page. Your H1 tag should also contain the keyword or phrase you want to rank for.
Most website platforms set your H1 tag by default, however, it’s always a good idea to double check it. Some themes might leave this important element out of the post if you’re not careful.
To see if your post is using an H1 tag, take a look at the source code. In Google Chrome, you can view any page’s source code by right-clicking on the page and selecting “View Page Source.”

Use Short and Sweet URLS That Include Your Target Keyword
Search engines like Google rely on more than just the post title when figuring out what a post is about. They also look at the post’s URL. Recent tests show that smaller, keyword-rich URLs perform better in search rankings.
For example, if your website posts URL includes the date (something like example.com/2016/06/05/seo/your-post-title is common among WordPress sites), consider dropping the date in the URL.
Ideally, you want to shoot for something like example.com/your-post-title- that-includes-your-target-keyword.
Link to Other Authoritative Websites within Your Industry
While it’s true that Google likes to see other websites linking to your website posts, it’s also important to be part of a community and sharing your knowledge.
If you’re not linking to other relevant websites or you’re “nofollowing” your links, you start to look like an island in the vast ocean that is the internet. Don’t be “that guy,” be a team player! Consider linking to other authoritative websites within your industry or niche that will add value for your visitors.
As an added bonus, you could also reach out to the sites you’ve linked to and let them know you’ve linked to them. Sometimes they’ll return the favor and link back to you or at least share your post with their audience.
Link to Your Own Pages or Other Posts You’ve Written
One of the biggest obstacles most websites fail to overcome is their Bounce Rate. A Bounce Rate is a percentage of visitors who leave your website on the same page they entered your website on, without visiting any other pages.
A high bounce rate tells Google that your website might not deliver quality information to the users it sends your way and it will quickly drop your search rank.
When writing a blog post, try and think of other posts you may have written in the past that also relate to the subject you’re writing about and link to them. If a visitor likes your content, they are likely to follow your links to read other posts you’ve written too. Wikipedia is great at doing this – check out the image below for an example.
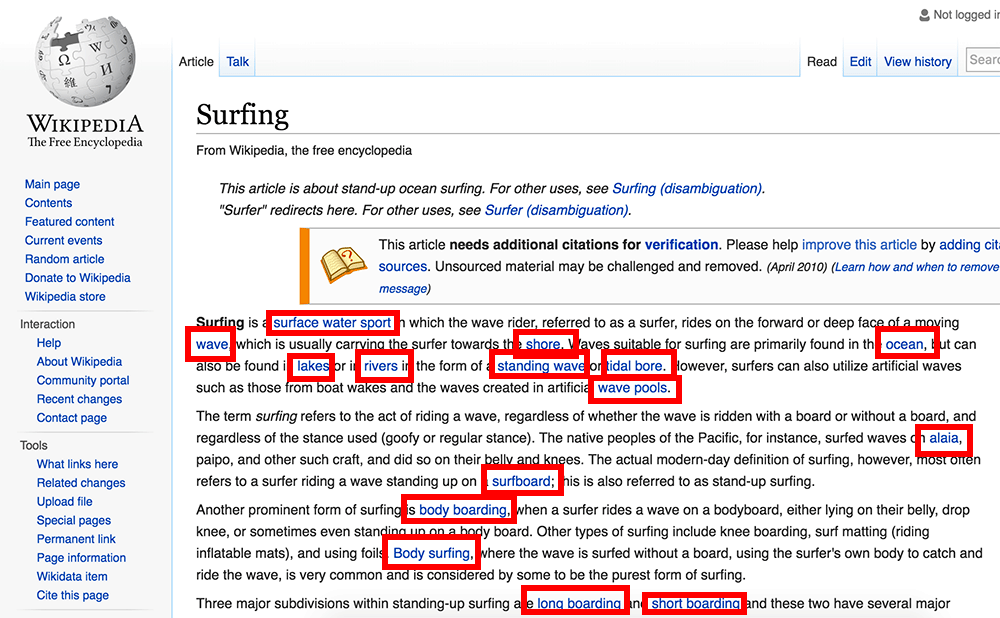
This is an easy way to cut your bounce rate while still providing value to your visitors. A good rule of thumb is to try and include 2-3 internal links per post.
Write At Least 1500 – 2000 Words If You Don’t Already Have a Massive Following
While there are plenty of successful blogs out there crushing it with short content (a few hundred words or so), they are not the norm. Guys like Seth Godin, Disney, and IFL (I F****** Love Science) regularly write short content and experience success, but a lot of it has to do with the authority they’ve built within their industries. If you’re just getting started or still building your fanbase, you’re better off to write long content to engage your readers and get more shares on social media. The team over at OkDork.com analyzed the top 10% most shared posts on social media:

This is especially important if your target keywords or phrases are competitive. Writing at least 1500 words in your posts infers credibility and your expertise on a given subject. It also gives search engines more to go off when indexing your post.
Include Images and Video
Including multimedia like images and videos in your posts doesn’t directly effect your ranking but it does affect signals the search engines look at when determining page rank. One such signal is the average length of time users spend on your pages. Another signal is the number of times your post or page has been shared on social media sites.
Let’s face it, people are visually driven and visitors are much more likely to engage with your content and share it when you include images or video.
A solid rule of thumb is to include an image (related to the content) about every 350 words. So, doing little math, content that contains ~1500 words should have 4 or 5 images sprinkled in.
Optimize Your Images
Speaking of images, you should make sure all your images include proper Alt and Title tags. These tags help the search engines understand what your image is about and it will give them more content to crawl and index.
Your Alt and Title tags should be relevant to the image with which they’re associated and should describe the image in a few words.
If the image is actually related to your target keyword(s) then it’s ok to include them in your tags. If the image has nothing to do with your target keyword(s), do not include them in your tags just for the sake of writing them again. Keep your Alt and Title tags short and sweet like your URLs and make sure they accurately describe the image.
Cut Page Load Time
Page load speed is an area of SEO that Google has been pretty blunt about. A site that loads slowly will have trouble ranking well.
Your page load speed also affects your user experience too. Pages that take longer to load tend to have higher bounce rates and lower average time on page.
A few quick tips to help your loading times:
Use Gzip (https://www.gnu.org/software/gzip/), a software application for file compression, to reduce the size of your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files that are larger than 150 bytes.
Minify and combine your CSS and JS files. This alone will give you a noticeable speed increase as well as reduce the number of HTTP requests.
Check out Google’s Page Speed Tool over at https://developers.google.com/speed/pagespeed/ for extra tips and recommendations.
Use Modifiers In Your Title Tag
What the heck is modifier? Modifiers are words like “buy”, “review”, “best”, “cheap”, “2016”, etc. They are words people combine with keywords or phrases while they’re searching online.
For example, if you’re looking for a new camera, you might catch yourself Googling the phrases “Best DSLR cameras” or “camera reviews.” A good way to find modifiers or other LSI Keywords (synonyms) related to your target keyword is scroll down to the bottom of a Google search where it lists related searches.

Adding modifiers to your target keyword or using some of these terms within your post is a great way to take advantage of those long tail searchers.
Mobile-friendly is a Must
We live in a world where people can browse the internet at any time, from a variety of devices. Also, websites that are not mobile-friendly will have a difficult time showing up in searches done on a mobile device, thanks to previous Google update.
Make sure your website using mobile-friendly design. Google recommends using Responsive Web Design, in particular.
Encourage Comments on Your Blog
Going back to the “internet as a community” idea, people leaving blog comments on your posts is a good thing. Even if it means you have to police it a bit, Google likes to see engagement with readers. A healthy comment section by itself isn’t a major factor but it can be an important piece of your On-page SEO strategy.
What Works for You?
Have you tried any of these techniques in the past or used others with success that weren’t mentioned here? Let me know about it by leaving a quick comment the comments section. Thanks!